Hello everyone!
We are back with another article. Today, we are going to talk about the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India in this blog. This Atlas was recently released by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change. We will discuss the major points of this atlas. Alongside, we will also talk about desertification and land degradation, its causes, its impacts and measures to curb it.
So let’s start with looking at the key points of the Atlas.
About the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas
- Recently, the Minister of State released the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas. It was released on the occasion of World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought (17th June).
- It has been published by Space Application Centre, ISRO, Ahmedabad.
- It presents state-wise desertification and land degradation status maps depicting land use, process of degradation and severity level.
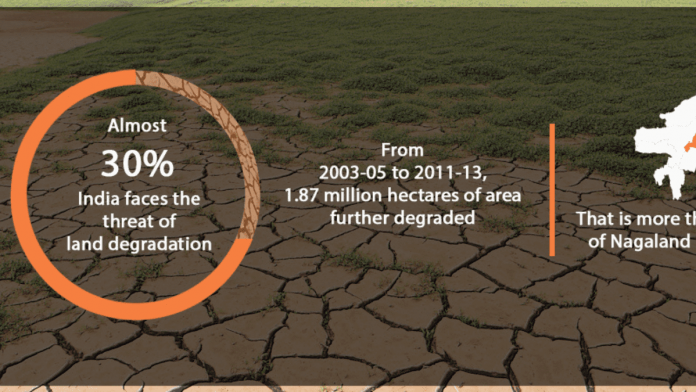
- It also provides the change analysis for the duration of 15 years, from 2003-05 to 2018-19.
- It is one of the outcomes of an ongoing MoEF&CC sponsored national project entitled, “Desertification Status Mapping of India”
- It has been prepared using Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) Advanced Wide Field (AWiFS) of 2011-13 and 2003-05 time frames in the GIS environment.
- It reveals that 96.40 mha* area of the country is undergoing process of land degradation. This figure is 29.32% of the Total Geographic Area (TGA) of the country during 2011-13. While during 2003-05 the area undergoing process of land degradation was 94.53 mha.
| *mha = million hectare |
Source: Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India
Significance of the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas
- The Atlas is helpful in identifying those areas where desertification is increasing year after year.
- It will help in prioritizing areas to be taken up minimizing the impact of land degradation and desertification.
- It will help to strengthen the envisaged National Action Plan for achieving land restoration targets.
Moving on, we will now see what Desertification is, its causes, its impact and measures to curb it.
What is Desertification?
Desertification is the degradation process by which the biological productivity of drylands (arid and semiarid lands) is reduced. It happens due to natural or manmade factors. Desertification takes place when a particular type of biome converts into a desert biome.
Causes of Desertification
- Man-made Causes:-
- Urbanization: It increases the demand for resources and puts pressure on the land which in turn reduces its productivity.
- Overgrazing: It reduces the usefulness, productivity, and biodiversity of the land.
- Deforestation: Cutting down trees for development activities reduces the fertility of the land.
- Farming Practices: Nowadays, Farming practices are exploiting land resources. Heavy tilling and overirrigation disturb the mineral composition of the soil. Practices like Slash and burn agriculture expose the state to soil erosion hazards.
- Climate change: Climate change is getting accelerated due to human activities. It may aggravate desertification through alteration of spatial and temporal patterns in temperature, rainfall, solar radiation and winds.
- Overexploitation of Resources: Increasing demand for land resources due to issues like overpopulation leaves the land vulnerable to desertification.
- Mining: Mining is another big reason for desertification. Large amounts of resources have to be extracted by industries to meet our demand for material goods.
- Natural Causes:-
- Natural Disasters: Natural Disasters like floods, droughts, landslides result in Water Erosion and Displacement of fertile soil.
- Wind Erosion: It reduces the fertility of the soil making the land susceptible to desertification.
- Water Erosion: It results in Badland Topography which itself is an initial stage of desertification.
Impacts of Desertification
- Vegetation gets damaged and destroyed: Desertification reduces the ability of the land to support plant life. Loose soil buries plants or exposes their roots to the sun, so they cannot fulfill their function.
- Soil becomes Infertile: Desertification makes the soil infertile and barren.
- Decrease in Crop Yields: A major effect of desertification is the decrease in crop yields. Once land turns from arable to arid, it is often on longer suitable for farming purposes anymore.
- Increased vulnerability to natural disasters: Desertification makes natural disasters worse because it reduces natural resilience of ecosystems. Desertification also increases the vulnerability of whole regions to the unpredictable effects of climate change.
- Rise of famine, poverty and social conflicts: Desertification results in the destruction of natural ecosystems and the end of services they provide for us.
- Endangerment and Extinction of Species: Desertification results in a decline in population for which species may become endangered or even extinct.
- Poor Water Quality: If an area becomes a desert, the water quality is going to become a lot worse than it would have been otherwise.
Status of Desertification in India
- Population growth, urbanization, overgrazing, soil erosion, etc. are all the important factors that have caused desertification in India.
- 96 million hectares or close to 29% of India’s area is undergoing degradation.
- According to the Government’s data, India lost 31%, or 5.65 million hectares, of grassland area in a decade.
- The extent of degraded land in India is over 105 million hectares or about 32% of India’s areas.
- India has witnessed an increase in the level of desertification in 26 of 29 states between 2003-05 and 2011-13.
Measures taken to curb Desertification in India
Multiple steps and measures have been taken by the concerned authorities regarding curbing desertification in India. Some of the measures are:
- Command Area Development: It was launched in 1974 which is coordinated by the Ministry of Water Resources for its implementation. It aims at improving the irrigation potential through water management.
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme: It was launched in 1989-90. It aims to restore ecological balance by harnessing, conserving and developing degraded natural resources with the creation of Rural Employment. It was named “Hariyali Guidelines” in 2003.
- Desert Development Programme: Implemented by the Ministry of Rural Development, it was launched in 1995 to minimize the effects of drought in the country.
- India also became a signatory to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) in 1994.
- National Afforestation Programme: It was implemented by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in the year 2000.
- National Action Programme to Combat Desertification: It was prepared in 2001 to address issues of increasing desertification and to take appropriate actions.
- Fodder and Feed Development Scheme: It aims to improve degraded grassland and also the vegetation cover of problematic soils like saline, acidic and heavy soil. It was launched in 2010.
So this was all about today’s blog. We have covered all the major points related to the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India. Furthermore, we have discussed in detail about desertification along with its causes and impacts. We have also talked about the status of desertification in India and measures taken to tackle it.
Hope you find this blog interesting and informative. For more such blogs, stay tuned!